হিন্দুস্তানী ভাষা
হিন্দুস্তানী (দেৱনাগৰী: हिंदुस्तानी) হৈছে এটা বহুকেন্দ্ৰিক ভাষা যাৰ দুটা মানক উপভাষা, হিন্দী (অধিকভাৱে সংস্কৃতকৃত) আৰু উৰ্দু (বেছি পৰিমাণে ফাৰ্চী- আৰবীকৃত)। ফলত ইয়াক হিন্দী-উৰ্দু বুলিও কোৱা হয়৷ ই ভাৰত আৰু পাকিস্তানৰ আভ্যন্তৰীণ সংযোগী ভাষা৷ মুঠতে উৰ্দু আৰু হিন্দীৰ মিশ্ৰণক সাধাৰণতে "হিন্দুস্তানী" বুলি কোৱা হয়।
| হিন্দুস্তানী | |
|---|---|
| হিন্দী–উৰ্দু | |
| |
 The word Hindustani in the Devanagari and Perso-Arabic scripts | |
| উচ্চাৰণ | [ɦɪnd̪ʊst̪ɑːniː] |
| থলুৱা অঞ্চল | ভাৰত আৰু পাকিস্তান |
| অঞ্চল | উত্তৰ প্ৰদেশ/দিল্লী (Hindustani Belt), Deccan (দক্ষিণ ভাৰত), পাকিস্তান[1] |
স্থানীয় ভাষিক |
L1 speakers: প্ৰায় 250 million (2011 & 2017 censuses)[2] L2 speakers: ~500 million (1999–2016)[2] |
ভাষা পৰিয়াল |
ভাৰত-ইউৰোপীয়
|
পূৰ্বসূৰী |
সৌৰসেনী প্ৰাকৃত
|
মান্য ৰূপ |
হিন্দী
উৰ্দু
|
| উপভাষা | *Deccani
|
| লিখন প্ৰণালী | |
সংকেতিক ৰূপ |
Indian Signing System (ISS)[4] |
| আধিকাৰিক স্থিতি | |
আধিকাৰিক ভাষা |
|
নিয়মাধীন হয় |
|
| ভাষা সংকেত | |
| ISO 639-1 | hi – Hindiসাঁচ:ISO639-1 – Urdu |
| ISO 639-2 | hin – Hindiসাঁচ:ISO639-2 – Urdu |
| ISO 639-3 | Either: hin – Hindi urd – Urdu |
| গ্লোটোলগ | hind1270[8] |
| লিংগোৱাস্ফেয়াৰ | 59-AAF-qa to -qf |
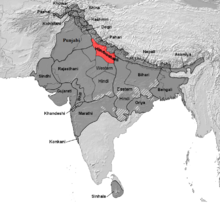 Areas (red) where Hindustani (Delhlavi or Kauravi) is the native language | |
চৰকাৰী মৰ্য্যাদা
সম্পাদনা কৰক১৯৪৭ চনৰ আগতে হিন্দুস্তানীক আনুষ্ঠানিকভাৱে ব্ৰিটিছ ৰাজে স্বীকৃতি দিছিল। স্বাধীনতাৰ পিছৰ সময়ছোৱাত অৱশ্যে হিন্দুস্তানী শব্দটোৱে মুদ্ৰা হেৰুৱাইছে আৰু ভাৰত বা পাকিস্তান চৰকাৰে ইয়াক কোনো আনুষ্ঠানিক স্বীকৃতি দিয়া নাই। ভাষাটোক ইয়াৰ পৰিৱৰ্তে ইয়াৰ মানক ৰূপ হিন্দী আৰু উৰ্দুৰ দ্বাৰা স্বীকৃতি দিয়া হৈছে।[9]
শব্দ-ভাণ্ডাৰ
সম্পাদনা কৰকহিন্দুস্তানী ভাষাত পাৰ্চী আৰু আৰবী মূলৰ প্ৰায় ৫,৫০০ শব্দ আছে।[10] ইংৰাজীৰ পৰাও যথেষ্ট সংখ্যক শব্দ ধাৰ কৰা হৈছে, লগতে ইউৰোপৰ অন্যান্য ভাষা যেনে পৰ্তুগীজ আৰু ওলন্দাজ (ডাচ)ৰ পৰাও কিছুমান শব্দ আছে।[11]
লিখন পদ্ধতি
সম্পাদনা কৰক| अ | आ | इ | ई | उ | ऊ | ए | ऐ | ओ | औ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ə | aː | ɪ | iː | ʊ | uː | eː | ɛː | oː | ɔː |
| क | क़ | ख | ख़ | ग | ग़ | घ | ङ | ||
| k | q | kʰ | x | ɡ | ɣ | ɡʱ | ŋ | ||
| च | छ | ज | ज़ | झ | झ़ | ञ | |||
| t͡ʃ | t͡ʃʰ | d͡ʒ | z | d͡ʒʱ | ʒ | ɲ[12] | |||
| ट | ठ | ड | ड़ | ढ | ढ़ | ण | |||
| ʈ | ʈʰ | ɖ | ɽ | ɖʱ | ɽʱ | ɳ | |||
| त | थ | द | ध | न | |||||
| t | tʰ | d | dʱ | n | |||||
| प | फ | फ़ | ब | भ | म | ||||
| p | pʰ | f | b | bʱ | m | ||||
| य | र | ल | व | श | ष | स | ह | ||
| j | ɾ | l | ʋ | ʃ | ʂ | s | ɦ |
| Letter | Name of letter | Transliteration | IPA |
|---|---|---|---|
| ا | alif | a, ā, i, or u | /ə/, /aː/, /ɪ/, or /ʊ/ |
| ب | be | b | /b/ |
| پ | pe | p | /p/ |
| ت | te | t | /t/ |
| ٹ | ṭe | ṭ | /ʈ/ |
| ث | se | s | /s/ |
| ج | jīm | j | /d͡ʒ/ |
| چ | che | c | /t͡ʃ/ |
| ح | baṛī he | h̤ | /h ~ ɦ/ |
| خ | khe | k͟h | /x/ |
| د | dāl | d | /d/ |
| ڈ | ḍāl | ḍ | /ɖ/ |
| ذ | zāl | z | /z/ |
| ر | re | r | /r ~ ɾ/ |
| ڑ | ṛe | ṛ | /ɽ/ |
| ز | ze | z | /z/ |
| ژ | zhe | ž | /ʒ/ |
| س | sīn | s | /s/ |
| ش | shīn | sh | /ʃ/ |
| ص | su'ād | s̤ | /s/ |
| ض | zu'ād | ż | /z/ |
| ط | to'e | t̤ | /t/ |
| ظ | zo'e | ẓ | /z/ |
| ع | ‘ain | ‘ | – |
| غ | ghain | ġ | /ɣ/ |
| ف | fe | f | /f/ |
| ق | qāf | q | /q/ |
| ک | kāf | k | /k/ |
| گ | gāf | g | /ɡ/ |
| ل | lām | l | /l/ |
| م | mīm | m | /m/ |
| ن | nūn | n | /n/ |
| ں | nūn ghunna | ṁ or m̐ | /◌̃/ |
| و | wā'o | w, v, ō, or ū | /ʋ/, /oː/, /ɔ/ or /uː/ |
| ہ | choṭī he | h | /h ~ ɦ/ |
| ھ | do chashmī he | h | /ʰ/ or /ʱ/ |
| ء | hamza | ' | /ʔ/ |
| ی | ye | y or ī | /j/ or /iː/ |
| ے | baṛī ye | ai or ē | /ɛː/, or /eː/ |
তথ্যসূত্ৰ
সম্পাদনা কৰক- ↑ "The History of the Urdu Language Together with Its Origin and Geographic Distribution". International Journal of Innovation and Research in Educational Sciences খণ্ড 2 (1). https://www.ijires.org/administrator/components/com_jresearch/files/publications/IJIRES-154_final.pdf.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "Hindi" L1: 322 million (2011 Indian census), including perhaps 150 million speakers of other languages that reported their language as "Hindi" on the census. L2: 274 million (2016, source unknown). Urdu L1: 67 million (2011 & 2017 censuses), L2: 102 million (1999 Pakistan, source unknown, and 2001 Indian census): Ethnologue 21. Hindi at Ethnologue (21st ed., 2018). Urdu at Ethnologue (21st ed., 2018).
- ↑ Gangopadhyay, Avik (2020). Glimpses of Indian Languages. Evincepub publishing. পৃষ্ঠা. 43. ISBN 9789390197828.
- ↑ Norms & Guidelines Archived 13 January 2014 at the Wayback Machine, 2009. D.Ed. Special Education (Deaf & Hard of Hearing), [www.rehabcouncil.nic.in Rehabilitation Council of India]
- ↑ The Central Hindi Directorate regulates the use of Devanagari and Hindi spelling in India. Source: Central Hindi Directorate: Introduction Archived 15 April 2010 at the Wayback Machine
- ↑ "National Council for Promotion of Urdu Language". www.urducouncil.nic.in. http://www.urducouncil.nic.in/.
- ↑ Zia, K. (1999). Standard Code Table for Urdu Archived 8 April 2019 at the Wayback Machine. 4th Symposium on Multilingual Information Processing, (MLIT-4), Yangon, Myanmar. CICC, Japan. Retrieved on 28 May 2008.
- ↑ Hammarström, Harald; Forkel, Robert; Haspelmath, Martin, eds (2017). "Hindustani". Glottolog 3.0. প্ৰকাশক Jena, Germany: Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History. http://glottolog.org/resource/languoid/id/hind1270.
- ↑ Schmidt, Ruth L (2003). Cardona, George. ed. Urdu. Routledge. পৃষ্ঠা. 318–319. ISBN 9780700711307.
- ↑ Kuczkiewicz-Fraś, Agnieszka (2008). Perso-Arabic Loanwords in Hindustani. প্ৰকাশক Kraków: Księgarnia Akademicka. পৃষ্ঠা. x. ISBN 978-83-7188-161-9.
- ↑ Chandola, Anoop Chandra (1963). "Some Linguistic Influences of English on Hindi". Anthropological Linguistics খণ্ড 5 (2): 9–13. ISSN 0003-5483. https://www.jstor.org/stable/30022405.
- ↑ Kachru, Yamuna (2006), Hindi, John Benjamins Publishing, p. 17, ISBN 90-272-3812-X